Natural honey not only delights the sweet flavourful taste but also holds significant nutrition value and health-enhancing properties. Most of natural honey is crafted by bees from the secreted nectars of diverse flowers, known as blossom or multi-floral honey. Another less common variant is honeydew or forest honey, stems from the exudates of plant sucking insects know as aphids. This insight highlights the unique health benefits of natural honey, making them valuable additions to a healthy diet.
Natural Sources of Nutritions
The precise composition of raw honey varies across different geographical regions influenced by the botanical sources available to the bees, which in turn, reflects their dietary preferences. Its primary components are sugars, predominantly fructose and glucose, accompanied by small amounts of fructo-oligosaccharides. Additionally, natural honey encompasses a rich spectrum of amino acids, vitamins, minerals and enzymes (Ajibola, Chamunorwa, & Erlwanger, 2012). Each spoonful of honey offers a symphony of nutrients that work in harmony to nourish and fortify the body.
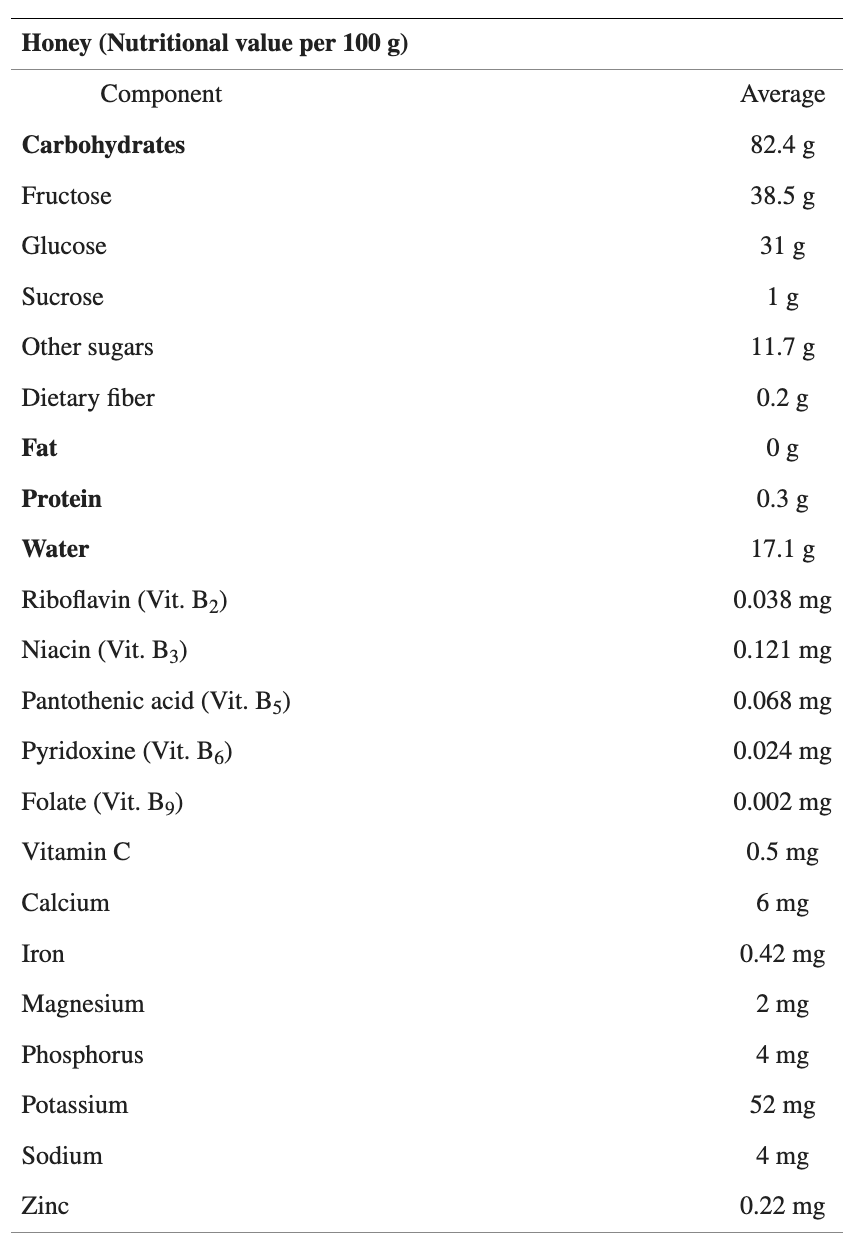
Figure: Average composition of Natural Honey per 100g (Eteraf-Oskouei & Najafi, 2013)
Digestion and Absorption
Natural honey has been proven to assist with digestion and absorption. Its enzymes aid in breaking down carbohydrates such as sugars and starches. Unlike refined sugars, which require digestion before absorption, honey's simple sugar molecules can be directly absorbed into the system, providing a quick source of energy. Moreover, honey acts as a prebiotic, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, which in turn supports digestive health. Studies have shown that honey can increase populations of beneficial bacteria like Bifidobacteria and lactobacilli in both laboratory and animal models, highlighting its potential as a digestive aid. Moreover, honey's provision of readily absorbable calcium can contribute to bone health, further enhancing its nutraceutical benefits for overall well-being (Ajibola, Chamunorwa, & Erlwanger, 2012).
Antioaxidant
The antioxidant properties of natural honey make it a valuable ally in combating oxidative stress, a known contributor to various diseases. Rich in flavonoids, phenolic acids and ascorbic acid, honey provides a synergistic antioxidant effect that can help prevent molecular transformations and gene mutations caused by radicals. Studies suggest that honey's antioxidant activity may even rival that of synthetic preservatives, making it a potential natural alternative for food preservation. The antioxidant activity of honey is influenced by its botanical origin, with darker honey varieties generally exhibiting higher levels of total phenolics and greater antioxidant capacity (Ajibola, 2015). These findings highlight honey's potential to support overall health by providing protection against oxidative damage at the cellular level.
Closing Remarks
Honey is not only a delicious sweetener but also has multiple health benefits. Rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, honey supports overall wellness by boosting the immune system, aiding digestion, and promoting wound healing. Its natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties make it an effective remedy for various ailments, while its soothing qualities can provide relief for sore throats and coughs. Incorporating natural honey into daily diet can contribute significantly to maintaining good health and enhancing quality of life.

At Hakada, we are committed to provide our customers with the 100% natural honey solutions. Though our strong network with beekeepers, we are able to acquire diverse types and process to meet specification. For product specification and exclusive sales, please reach out to us at inquiry@hakadatrading.com.
References
Ajibola, A. (2015). Novel insights into the health importance of natural honey. Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, 22(5), 7-22. https://doi.org/10.21315/mjms2015.22.5.2
Ajibola, A., Chamunorwa, J. P., & Erlwanger, K. H. (2012). Nutraceutical values of natural honey and its contribution to human health and wealth. Nutrition & Metabolism, 9(61). https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-7075-9-61
Eteraf-Oskouei, T., & Najafi, M. (2013). Traditional and modern uses of natural honey in human diseases: A review. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, 16(6), 731-742. https://doi.org/10.22038/IJBMS.2013.8755